
Medications such as diuretics for treating high blood pressure, medications for depression and over-the-counter medications containing decongestants or antihistamines also can cause urinary incontinence.
Temporary causes of urinary incontinence: Temporary episodes of urinary incontinence may be caused by drinking too much alcohol or caffeine, constipation, or depression. Therefore, any severe injury to the spine can lead to urinary incontinence. Spinal injury: Nerve impulses transmitted between the brain and bladder usually come through the spine. The conditions make it difficult for nerve signals to be sent and received between the central nervous system(CNS) and the bladder, increasing the risk of urinary incontinence. Neurological diseases: The two most common neurological diseases that may cause urinary incontinence are Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis. Stroke also can make it difficult for a man to get up and walk to the bathroom, which also contributes to urinary incontinence. When stroke occurs there may be loss of muscle control and decreased sensation, which may lead to urinary incontinence. Stroke: Stroke refers to brain damage that is caused by decreased flow of blood to the brain because of a clot or a leaking blood vessel. Obesity, which is quite common in type II diabetes, can make urinary incontinence worse by exerting more pressure on the bladder. It also can cause frequent urination or an overactive bladder. Diabetes: Diabetes can cause damage to the nerves or muscles controlling how the bladder opens and closes. Urinary tract infections: The infections can cause an overactive bladder, which may be characterized by urinary incontinence. Prostate surgery: The surgical removal of the prostate gland during the treatment of prostate cancer or BPH can damage or weaken the muscles controlling urine flow, resulting in stress urinary incontinence. As the prostate grows bigger, it compresses the urethra and may impede the flow of urine, resulting in urinary incontinence. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Most men experience prostatic enlargement after the age of 40. The common underlying factors in urinary incontinence include: Anything that affects the muscle or nerve function of the sphincter can result in urinary incontinence. At the opening of the bladder is a muscle called the urinary sphincter, which controls the opening and closing of the bladder. Other common causes of male urinary incontinence are muscle and nerve control problems. The problem with the prostate gland is that it tends to increase in size as a man grows older and extend to the point of impeding or slowing down the flow of urine from the bladder. 
The principal role of the prostate is adding fluid to the semen during ejaculation. The prostate, which is normally the size of an almond, is found at the opening of the bladder. However, prostate gland problems and their treatment are often the most common causes of UI in older men. There is no standout factor among the causes of urinary incontinence in men. It can happen even when you do not feel the urge to urinate. Overflow incontinence: This is the unintentional loss of urine characterized by dribbling or leakage of urine in small quantities.
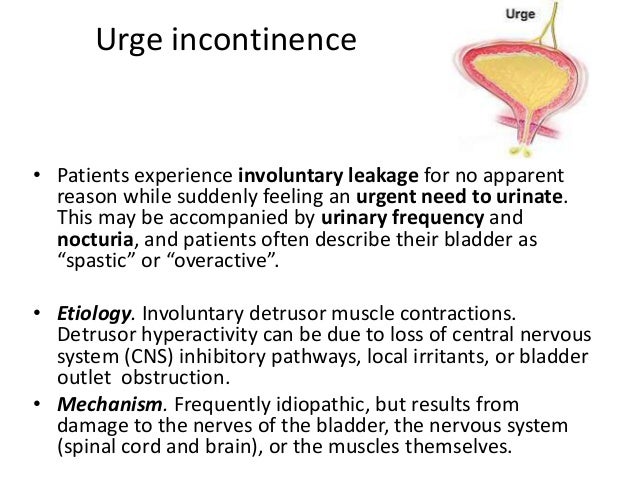
 Urge incontinence: This is the accidental loss of urine that occurs when the need to urinate is too strong and uncontrollable.
Urge incontinence: This is the accidental loss of urine that occurs when the need to urinate is too strong and uncontrollable. 
Stress incontinence: It is the leakage of urine that occurs when the pressure inside the bladder increases when doing things such as sneezing, coughing, climbing or lifting.There are three major types of urinary incontinence in men: Urinary incontinence is not a disease but just the symptom of an underlying condition, such as a prostate problem, injury to the urinary tract or a disease of the nerve system. In the United States, up to 17 percent of men may suffer from urinary incontinence, with the frequency of the condition increasing with age. Urinary incontinence in men is the unintentional or accidental loss of urine.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
